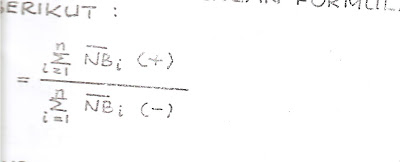GROSS B/C adalah perbandingan antara benefit kotor yang telah di discount dengan cost secara keseluruhan yang telah di discount
GROSS B/C =
Ratio ini menunjukkan :
Gross B/C ratio > 1 ----> FISIBEL (GO)
Gross B/C ratio < 1 ----> Tidak Fisibel (NO GO)
Gross B/C ratio = 1 ----> BEP
Selasa, 29 November 2011
Senin, 28 November 2011
STUDY KELAYAKAN BISNIS - PROFITABILITY RATIO (PR)
Profitability ratio merupakan suatu ratio antara selisih benefit dengan biaya operasi dan pemeliharaan di banding dengan jumlah investasi.
Nilai dari masing-masing variabel dalam bentuk present value atau nilai yang telah di discount dengan discount capital yang berlaku dalam masyarakat , dapat di tulis dalam formula sbb :
 |
| Profitability Ratio |
Nilai Waktu Dari Uang (TIME VALUE OF MONEY)
Jika suatu investasi yang ditanamkan dengan suatu suku bunga tertentu pada suatu selang waktu tertentu. Maka uang yang di tanam itu jumlahnya akan membesar pada saat uang itu di ambil pada akhir selang penanaman kenyataan ini menunjjukkan bahwa waktu dan suku bunga berpengaruh terhadap julah yang di terima pada ahir selang waktu dari hasil penanaman semula.
Jika suku bunga 20% per tahun, Rp.1.000.000 yang di investasikan pada sebuah bank, makan akan di kembalikan sebesar Rp.1.000.000 di tambanh dengan bunga Rp.200.000 ( Rp 1.000.000 x 20%= Rp. 1.200.000,- ) jadi Rp 1 Jt hari ini akan bernilai lebih banyak dari Rp. 1 Jt satu tahun dari sekarang, dan dengan suku bunga 20% kita mengetahui bahwa Rp 1jt benar2x ekuivalen dengan Rp.1.200.000 setahun dari sekarang.
Jumlah rupiah yang sama pada batas waktu yang berbeda mempunyai nilai yang berbeda selama bunga yang dapat di hasilkan melebihi nol membuktikan pada kita bahwa uang mempunyai nilai waktu. Jelaslah, nilai waktu dari uang adalah suatu hubungan di antara nilai uang hari ini dan nilainya pada suatu saat di masa datang dengan mempertimbangkan bunga.
NET BENEFIT COST RATIO (NET B/C RATIO)
Net B/C ratio merupakan perbandingan antara net benefit yang telah di discount positif (+) dengan net benefit yang telah di discount negatif (-) , dengan formula sebagai berikut :
NET B/C =
NET B/C =
Jika nilai Net B/C lebih besar dari 1 (satu) berarti gagasan usaha/proyek tsb layak untuk di kerjakan dan jika lebih kecil dari 1 (satu) berarti tidak layak untuk dikerjakan. Untuk NET B/C sama dengan 1(satu) berarti cash in flows sama dengan cash outflows, dalam present value di sebut dengan BREAK EVEN POINT (BEP), yaitu TOTAL COST = TOTAL REVENUE.
Senin, 21 November 2011
INTERNAL RATE OF RETURN
IRR adalah suatu discount rate yang menghasilkan NPV sama dengan NOL.
Dengan demikian apabila :
1. Hasil perhitungan IRR > dari Sosial Opportunity Cost Of Capital (SOCC) = Proyek Fisible.
2. IRR = SOCC = Break even Point (BEP)
Formula :
IRR = I1 + [ NPv1 / ( NPv1-NPv2 ) ] [ I1 -I2 ]
I1 = Discount Rate yang menghasilkan NPV (+)
I2 = Discount rate yang memberkan NPV (-)
Kesimpulan :
"Berdasarkan percobaan , Nilai IRR berada di antara Nilai NPV positif dan Nilai NPV negatif yaitu pada NPv = 0,
Dengan demikian apabila :
1. Hasil perhitungan IRR > dari Sosial Opportunity Cost Of Capital (SOCC) = Proyek Fisible.
2. IRR = SOCC = Break even Point (BEP)
Formula :
IRR = I1 + [ NPv1 / ( NPv1-NPv2 ) ] [ I1 -I2 ]
I1 = Discount Rate yang menghasilkan NPV (+)
I2 = Discount rate yang memberkan NPV (-)
Kesimpulan :
"Berdasarkan percobaan , Nilai IRR berada di antara Nilai NPV positif dan Nilai NPV negatif yaitu pada NPv = 0,
Minggu, 13 November 2011
STUDI KELAYAKAN BISNIS ( BUSINESS FEASIBILITY STUDY ) : NPV
NET PRESENT VALUE
Definition :
A lot of investment criteria used in assessing whether a project is feasible or not.
NET BENEFIT NPV calculation is that has been discounted using SOCIAL OPPORTUNITY COST OF CAPITAL (SOCC) as the discount factor.
SOCC is a benefit that is lost due to capital project is used forsomething. The meaning of the lost benefits are benefits that can be obtained with the use of capital in the most profitable alternative use of which has not been met.
STUDI KELAYAKAN BISNIS ( BUSINESS FEASIBILITY STUDY ) : ANALYS CRITERIA
IV ANALYSIS CRITERIA
Definition :
The purpose of the calculation of investment criteria is to determine the extent to which business ideas (projects) are in the plan may provide benefits (benefits), both in view of the financial benefit and social benefit.
The results of calculation of the investment criteria is the indicatorof capital invested, ie the ratio between the received BENEFITTOTAL TOTAL COST with that issued in the form of economic life during the PRESENT VALUE.
CRITERIA INVESTMENT CRITERIA
1. NET PRESENT VALUE (NPV)
2. INTERNAL RATE OF RETURN (IRR)
3. NET COST BENEFIT RATIO (NET B / C)
4. COST BENEFIT RATIO GROSS (GROSS B / C)
5. PROFITABILITY RATIO (PR)
ANALYSIS OF PROJECT DECISION
1. ACCEPT OR REJECT THE PROJECT
2. CHOOSE ONE OF THE MOST OR SEVERAL PROJECTSWORTH TO DO
3. SET SCALE OF PRIORITY PROJECTS WORTH.
STUDI KELAYAKAN BISNIS ( BUSINESS FEASIBILITY STUDY ) : PERT
III. P E R T
PERT: a method of analysis that was created to help thescheduling and supervision of projects that are complex and require certain activities to be performed in the order of a particular sequence.
incremental Cost
Is added as a result of the reduced cost of one unit of time.
COST Ic = Δ / Δ TIME = (Cc - Cn): (Tn - Tc)
Cn = Normal Cost
Cc = Cost Acceleration
Tn = Normal Time
Time After Accelerated Tc (Crash Time)
STUDI KELAYAKAN BISNIS ( BUSINESS FEASIBILITY STUDY ) : PROYEK
II. PROJECT
Project: is a series of activities that use resources to obtain benefits (benefits) or an activity with expenses and with the hopeto obtain results that will come in time.
Project Evaluation: This is an activity that is assessed and select a variety of investments that may be developed in accordancewith the investment in own ability
Technical Aspects of Production: Aspects related to the construction project is planned well in view of the location factor,extensive production, production processes, use of technology(machinery / equipment), as well as environmental conditionsassociated with the production process.
Investment Costs: Costs that need in the construction of the project.
Working Capital: It is cost issued to finance business activitiesafter the construction project is completed.
Economic Analysis: is a project which saw an activity from the point of the overall economy.
Financial Analysis: Analysis of angles to see a project frominstitutions or entities that have a direct interest in the project orwho invest their capital into the project.
Project Benefits: The revenue generated by a project beforededucting expenses is issued.
Direct Benefits: The benefits received as a result of the project,such as the rising value of production of goods or services,changes in shape, lower costs, and so forth.
Indirect benefits: the benefits of development projects are difficult to measure in monetary terms such as changing the mindset of society, environmental improvement, reduced unemployment, increased national security, stability of price level, and so forth.
STUDI KELAYAKAN BISNIS ( BUSINESS FEASIBILITY STUDY )
BUSINESS FEASIBILITY STUDY
I. INTRODUCTION
Definition:
Activities to assess the extent to which benefits can be obtained in executing a business activity / project
Objective:
Assess the feasibility of a business idea / this is aconsideration of whether the business / project is accepted or rejected.
Langganan:
Komentar (Atom)